Ghrelin and Weight Loss: The Ultimate Guide to Control Hunger
Body composition analysis showing lean mass vs fat mass ratio
Key Takeaways
- Ghrelin is your hunger signal - it rises before meals and drops after eating. Your goal isn't to eliminate it but to control its fluctuations.
- Protein is your strongest weapon - it's scientifically proven to suppress ghrelin and keep you full longer than any other macronutrient.
- Sleep deprivation causes ghrelin to spike dramatically while lowering leptin (your fullness hormone), setting you up for intense cravings the next day.
- Extreme calorie restriction triggers a survival response - your body floods with ghrelin to prevent starvation, making long-term dieting nearly impossible.
The Hunger Hormone Code: How Ghrelin Affects Weight Loss (And How to Finally Master It)
Ever felt like your own body is working against your weight loss goals? You eat a healthy meal, but an hour later, that familiar, gnawing hunger returns, demanding attention. It’s not a lack of willpower; it’s likely a powerful hormone calling the shots: ghrelin.
Many people think weight loss is just a simple game of “calories in, calories out.” But in my experience, helping countless individuals navigate their health journeys, I’ve seen that this is only half the story. The real secret often lies in understanding and managing the hormonal signals that drive our hunger and cravings.
This comprehensive guide isn’t just another science lesson. It’s a practical playbook designed to help you understand the “hunger hormone” and, more importantly, give you actionable strategies to work with it, not against it. By the end of this article, you will have a clear roadmap to reduce overpowering cravings and make your weight loss journey feel less like a battle and more like a partnership with your body.
Key Takeaways: Your Fast-Track to Ghrelin Control
For those short on time, here are the most critical insights you need to know about mastering ghrelin for sustainable weight loss:
- Ghrelin is a “Meal Initiator”: Its primary job is to tell your brain it’s time to eat. Levels rise before meals and fall after. The goal is not to eliminate it, but to manage its peaks and valleys.
- Protein is Your Best Ally: Protein is the most satiating macronutrient and has been shown to be highly effective at suppressing ghrelin levels, keeping you fuller for longer.
- Sleep Deprivation is a Ghrelin Trigger: Poor sleep dramatically increases ghrelin and decreases its counterpart, leptin (the “satiety hormone”), creating a perfect storm for cravings and overeating.
- Diets Can Backfire: Severe calorie restriction can cause your body to produce more ghrelin in an attempt to fight perceived starvation, making long-term dieting incredibly difficult.
- Strategic Habits Matter More Than Willpower: You can influence your ghrelin levels through what you eat, when you eat, how you exercise, and how you manage stress.
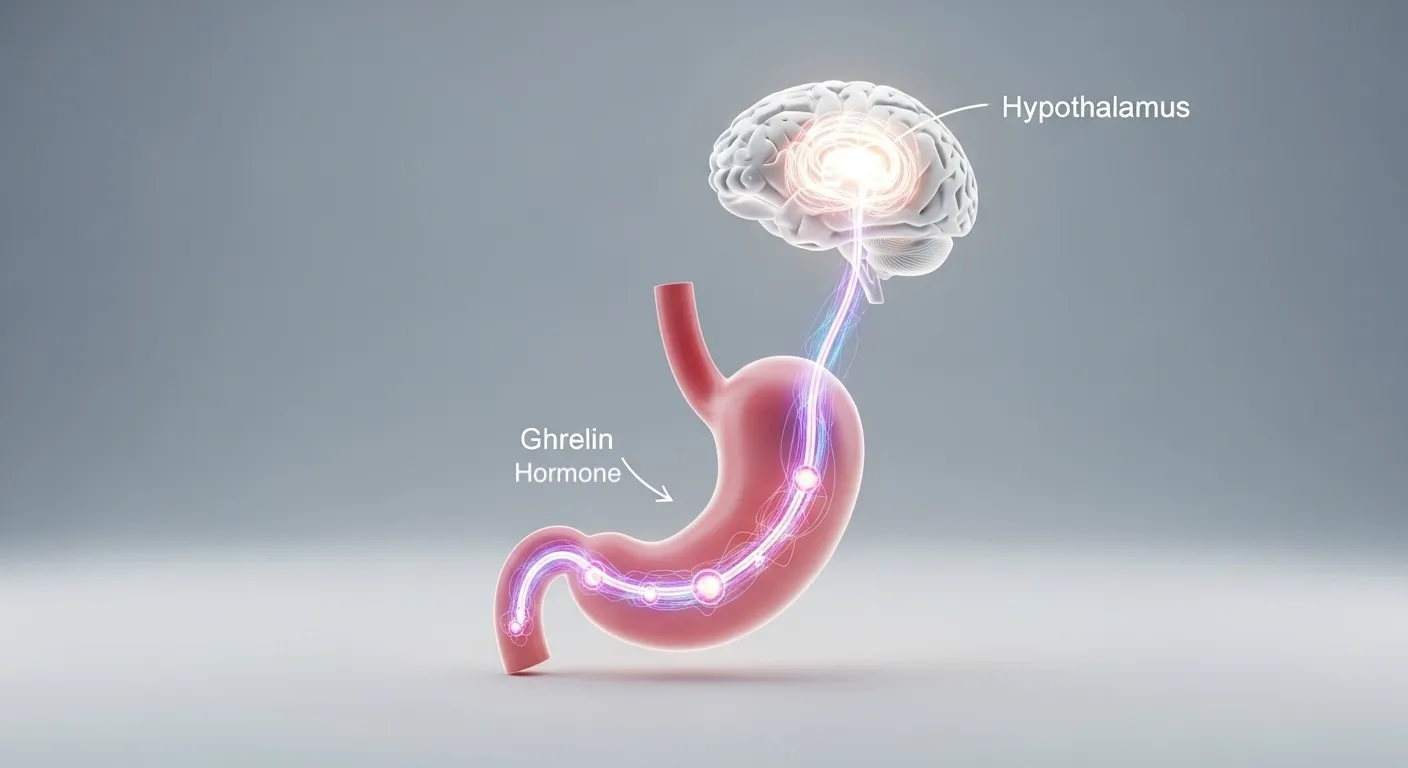
What Exactly is Ghrelin? Meet Your “Hunger Hormone”
Think of ghrelin as your body’s internal lunchtime bell. Primarily produced in the stomach, this hormone travels through your bloodstream to your brain, specifically to the hypothalamus, which is the control center for appetite. When your stomach is empty, it releases ghrelin, sending a powerful signal that says, “It’s time to seek out food.”
Once you eat and your stomach stretches, ghrelin production slows down, and the hunger signal fades. This elegant system is designed for survival, ensuring we seek energy when we need it. However, in our modern world, this system can easily become dysregulated, leading to persistent hunger that sabotages weight management efforts.
Understanding that ghrelin is a signal, not a weakness, is the first step toward regaining control.
The Ghrelin and Leptin See-Saw: Your Body’s Appetite Control System
Ghrelin doesn’t work in isolation. Its partner in crime is leptin, the “satiety hormone.” If ghrelin is the green light for eating, leptin is the red light.
- Ghrelin (The Accelerator): Says “Go, eat!” Rises when you’re hungry.
- Leptin (The Brake): Says “Stop, you’re full!” Rises when you’re satiated.
A healthy weight management system depends on the delicate balance of this hormonal see-saw. When they are in sync, you eat when you’re hungry and stop when you’re full. But when factors like poor sleep, chronic stress, or highly-processed diets disrupt this balance, ghrelin can start shouting while leptin whispers, leaving you feeling constantly hungry even when your body has enough energy.
[PRO-TİP: Stop thinking about “fighting” hunger. Start thinking about balancing your hunger and satiety hormones. This mindset shift is a game-changer for long-term success.]

Why Extreme Dieting Can Make You Hungrier: The Ghrelin Rebound Effect
Have you ever noticed that the deeper you get into a strict diet, the more ravenous you become? This isn’t your imagination. It’s a biological phenomenon known as the ghrelin rebound.
When you significantly cut calories for an extended period, your body’s survival instincts kick in. It perceives the calorie deficit as a threat and fights back by:
- Increasing Ghrelin Production: Your body literally screams for more food to combat the perceived famine.
- Decreasing Leptin Sensitivity: Your brain becomes less responsive to the “I’m full” signal.
This is why so many people experience a rebound in weight after a crash diet. Their hormonal environment makes overeating almost inevitable. A more sustainable approach focuses on nourishing your body with the right foods to naturally regulate ghrelin instead of simply starving it.
Mastering Your Ghrelin: 5 Actionable Strategies for Natural Hunger Control
Now for the practical part. Here are five powerful, science-backed strategies to help you manage your ghrelin levels and reduce hunger naturally.
1. Prioritize Protein and Fiber at Every Meal
If you remember one thing from this article, let it be this: protein is ghrelin’s number one enemy. Of the three macronutrients (protein, fat, carbs), protein is the most effective at suppressing ghrelin and promoting satiety.
- How it Works: Protein-rich meals slow down stomach emptying and trigger the release of other gut hormones that signal fullness to the brain.
- Actionable Step: Aim to include a quality protein source (like eggs, Greek yogurt, chicken, fish, lentils, or tofu) in every meal. Pairing it with fiber-rich vegetables or whole grains enhances the effect. This combination is the foundation of hormones that control appetite.

2. Make Sleep Your Non-Negotiable Priority
You can’t out-diet poor sleep. It’s one of the most significant disruptors of appetite hormones. Even one or two nights of insufficient sleep can cause ghrelin levels to spike.
- The Science: Studies consistently show that sleep-deprived individuals have higher ghrelin, lower leptin, and report increased hunger, especially for high-calorie, sugary foods.
- Actionable Step: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Create a relaxing bedtime routine, avoid screens an hour before bed, and ensure your bedroom is dark and cool. This is the most effective “ghrelin reset” you can perform each night.
3. Use Strategic Exercise (Don’t Overdo It)
Exercise has a fascinating dual effect on ghrelin.
- Short-Term Suppression: Intense exercise, like High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), can temporarily suppress ghrelin, which is why you might not feel hungry immediately after a tough workout.
- Long-Term Regulation: Consistent, moderate exercise helps improve leptin sensitivity and contributes to overall hormonal balance.
[PRO-TİP: A common mistake I see is using exercise as a license to eat anything. Instead, use the post-workout period of reduced hunger to rehydrate and plan a balanced, protein-rich meal for later. This leverages the exercise effect on ghrelin to your advantage.]
4. Manage Stress to Manage Cravings
Chronic stress is a major driver of emotional eating, and ghrelin plays a role here too. The stress hormone, cortisol, can increase ghrelin levels, leading you to seek comfort in “hyper-palatable” (salty, sugary, fatty) foods.
- Actionable Step: Find a stress-management practice that works for you. This could be a 10-minute daily meditation, a walk in nature, journaling, or deep breathing exercises. By managing cortisol, you indirectly help manage ghrelin.

5. The Truth About Intermittent Fasting and Ghrelin
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a popular tool, and its effect on ghrelin is a hot topic. Does intermittent fasting lower ghrelin? The answer is nuanced.
Initially, during the fasting window, ghrelin levels will rise as expected—that’s your body signaling it’s time to eat. However, many long-term practitioners of IF report that their bodies adapt. The ghrelin peaks become more predictable and manageable, essentially “training” the hunger hormone to appear only at designated eating times. For some, this provides a powerful sense of control over their hunger.
- Consideration: IF is not for everyone. If you have a history of disordered eating or certain medical conditions, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional. [İç link önerisi: Is Intermittent Fasting Right for You? A Beginner’s Guide]
Conclusion: Partner With Your Hormones, Don’t Fight Them
Understanding how ghrelin affects weight loss is about shifting your perspective. The relentless hunger you might be experiencing isn’t a moral failing; it’s a biological signal. And the great news is that you have the power to influence that signal.
By focusing on a diet rich in protein and fiber, prioritizing quality sleep, engaging in strategic exercise, and managing stress, you can create a hormonal environment that supports your goals. You can tame the hunger hormone and transform it from a saboteur into a predictable guide.
Your next step? Don’t try to change everything at once. Pick just one strategy from the list above—perhaps adding a protein source to your breakfast—and focus on it for the next week. Small, consistent changes are the key to mastering your hormonal health for good.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the best natural ghrelin blocker foods?
While no food can completely block ghrelin (as it's a necessary hormone), some are incredibly effective at suppressing its release. The best options are lean proteins (chicken breast, fish, eggs), high-fiber foods (oats, beans, avocados, apples), and healthy fats (nuts, seeds). These foods promote satiety and keep ghrelin levels lower for longer after a meal.
Why am I so hungry at night? Is it a ghrelin spike?
Nighttime hunger is often a combination of factors. Ghrelin does follow a circadian rhythm and can naturally rise in the evening. However, this is often amplified by not eating enough during the day (especially protein), dehydration, or habits like stress-related or bored eating. A balanced, protein-rich dinner can significantly help curb nighttime ghrelin spikes.
Does intermittent fasting permanently lower ghrelin?
Intermittent fasting doesn't permanently lower your baseline ghrelin. Instead, it can help regulate its rhythm. Over time, your body may adapt to only release significant ghrelin around your expected eating times, making hunger during the fasting window much more manageable. The feeling of control comes from this predictability.
What are some symptoms of a ghrelin hormone imbalance?
Symptoms of dysregulated ghrelin are often linked to persistent hunger. This can include intense cravings even after eating a full meal, constant thoughts about food, difficulty feeling full, and a tendency to overeat, particularly under stress or when tired.
Are there supplements that lower ghrelin?
The supplement market is complex, and direct, proven ghrelin-lowering supplements are not well-established for general use. Some research has explored compounds like Fenugreek fiber for their potential to increase feelings of fullness, which may indirectly influence the ghrelin/leptin system. However, focusing on whole foods, sleep, and lifestyle is a far more reliable and proven strategy.
